- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
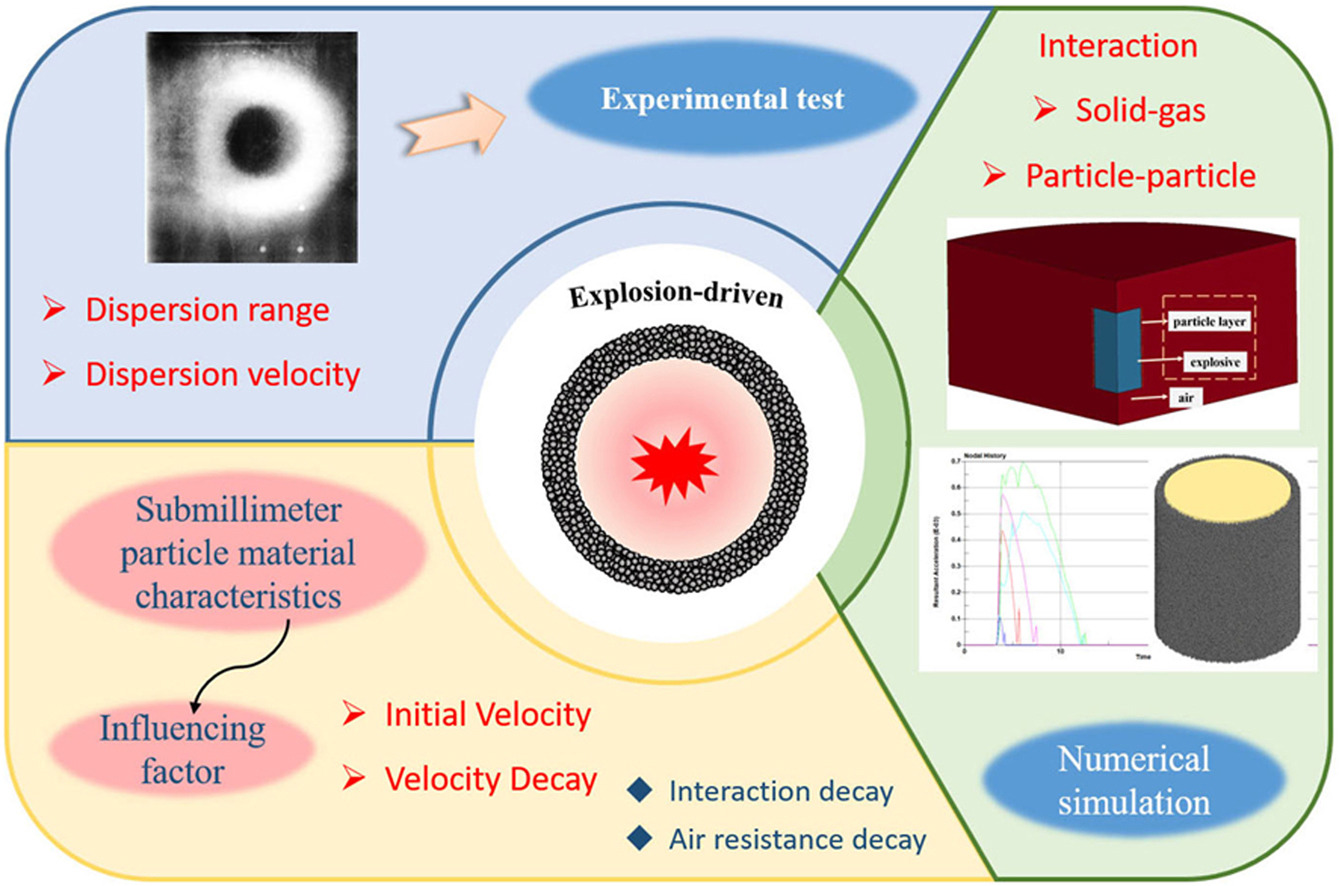
•A capture test (flash X-ray photography) for submillimeter particle dispersion was carried out.
•DEM-FEM simulation method of explosive driven particle dispersion was verified.
•Effect of particle material characteristics on velocity attenuation was discussed.
•Global velocity evolution of submillimeter particle under explosive loading was obtained.
Low collateral damage munitions incorporate tens of thousands of submillimeter heavy metal particles in the shell, replacing the conventional metal shell. These munitions achieve near-field damage capabilities comparable to that of conventional munitions, while relying on the dispersion decay characteristics of the particles to control the range of damage. However, the submillimeter size of particles poses significant challenger in analyzing explosion-driven scattering. In this study, X-ray test was used to capture the scattering and dispersion state of the particle groups driven by blast load. The scattering evolution was simulated using the discrete element method (DEM) coupled with the finite element method (FEM). The extended velocity field distribution was analyzed in terms of the two-phase flow forces governing particle decay, to reveal the velocity evolution during particle group scattering and qualitatively analyze its influencing factors. Ensuring the strength of the layer structure, results indicate that lower particle content in the structural shell promotes easier expansion and rupture, enhancing the scattering ability of the particle group. The initial particle velocity is determined by the explosive energy and the mass ratio of the composite shell to the explosive (M/C). Near-field explosion dynamics involve complex interactions among shock waves, blast products, and particles groups in a multiphase medium. In contrast, far-field behavior reflects particle decay driven by air resistance, which is related to the resistance characteristic time. This study presents a method for calculating particle group velocity evolution, offering valuable insights for the engineering design and effect assessment of low collateral damage munitions.