- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
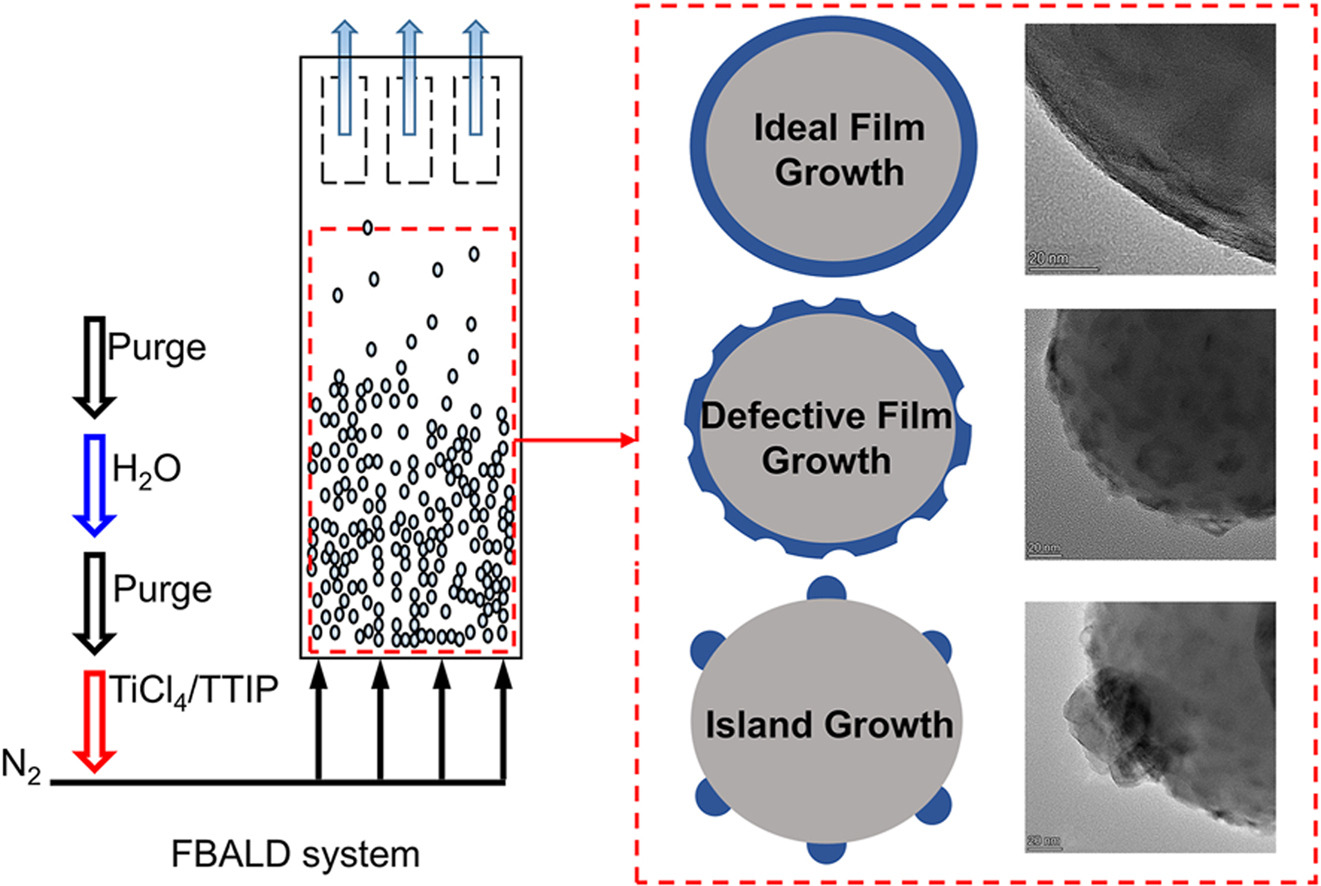
• Growth characteristics of FBALD-TiO2 under various conditions are investigated.
• FBALD-TiO2 forms films at 120–180 °C and islands at 240–300 °C.
• TiCl4 achieves higher GPC, whereas TTIP enhances film uniformity.
• FBALD yields more efficient SiO2@TiO2 photocatalyst than solution impregnation.
• Three typical growth modes of FBALD-TiO2 are summarized.
TiO2 is an ultra-wide bandgap semiconductor with excellent physical properties and promising applications in photocatalysis and photo-electrocatalysis. Fluidized bed atomic layer deposition (FBALD) is an effective method for depositing TiO2 films, offering precise thickness control. This study presents a comprehensive investigation into the growth characteristics and properties of TiO2 films on SiO2 particles prepared via FBALD, with a focus on the impact of cycle number, temperature, precursor concentration, pulse time, purge time and precursor component. The TEM images indicate that continuous and uniform TiO2 films are formed at 120 °C and 180 °C, whereas dispersed nanoscale TiO2 islands are observed at 240 °C and 300 °C. By increasing precursor supply or reducing N2 purge time, the film growth rate significantly increases. Additionally, increasing the precursor pulse time has a stronger effect on film growth, while decreasing the N2 purge time leads to more uneven film thickness growth. The core-shell structured SiO2@TiO2 photocatalysts synthesized using TiCl4 and TTIP as precursors both exhibit good photocatalytic degradation performance that, under 300 W xenon lamp irradiation for 60 min, the degradation efficiency of tetracycline hydrochloride (TC) reaches 95 % and 90 %, respectively. This performance surpasses that of catalysts prepared by solution impregnation method under the same mass fraction.