-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 106
-
Volume 105
-
Volume 104
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 106
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
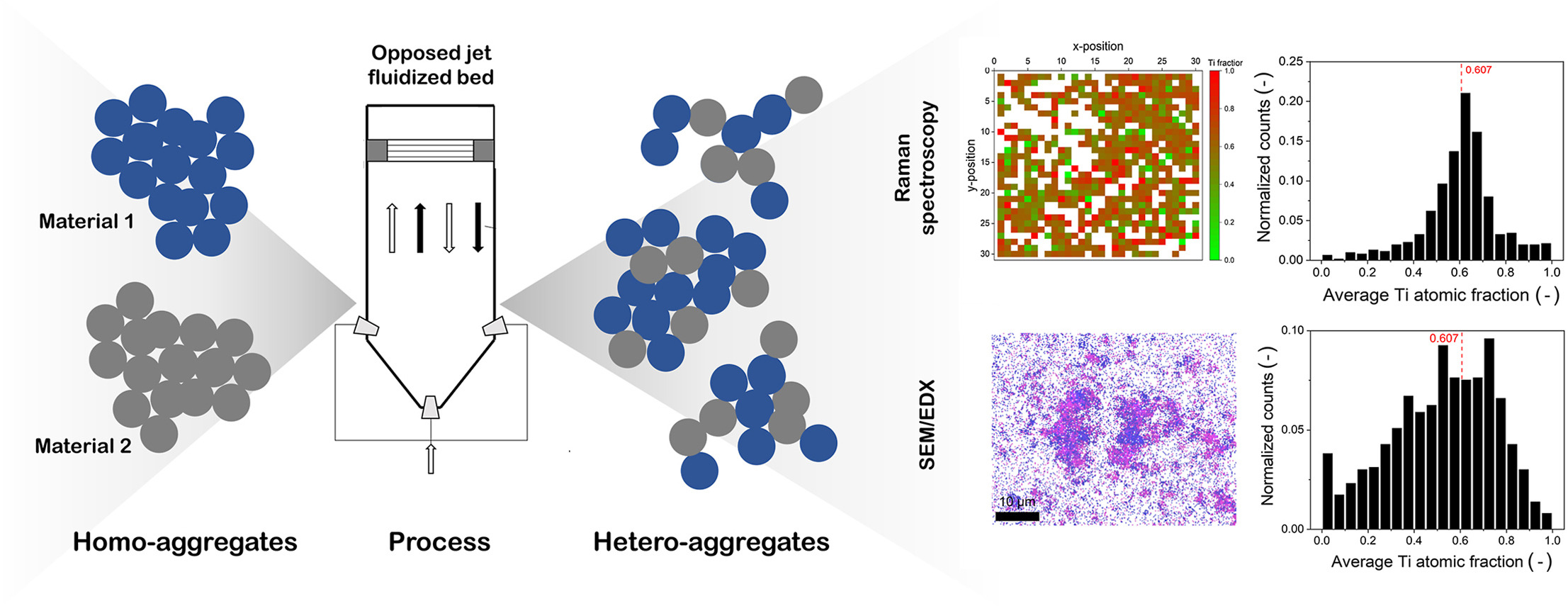
• Inter-aggregate mixing was successfully evaluated using Raman microspectroscopy and EDX.
• Compositional self-stabilization behavior was observed under all operating conditions.
• The processing time had a limited influence, suggesting rapid mixing stabilization.
• The final system composition is strongly dependent on the mass ratio and pressure.
The mixing quality in nanoparticulate systems plays a fundamental role in the functional enhancement of advanced materials. In this study, we evaluate the effectiveness of mixing TiO2 (rutile) and ZrO2 (monoclinic) nanopowders using Raman mapping and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy within a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Eighteen experiments were carried out in an opposed jet fluidized bed, varying process time, mass ratio, and Laval nozzle back pressure. Raman mapping enabled spatially resolved identification of phases, while SEM/EDX provided high-resolution elemental composition. Both techniques indicated good overall inter-aggregate mixing efficiency, especially at a mass ratio of 1:1, with average Ti atomic fractions close to 0.607. Quantitative comparison showed that Raman micro spectroscopy yielded lower relative deviations from the expected values and required simpler sample preparation, making it a practical choice for assessing mixing homogeneity. Deviations from the expected compositions were more pronounced at other mass ratios (especially 1:2), likely owing to differences in particle size, density, and aggregation tendencies. Finally, in contrast to previous intra-aggregate mixing studies, the current results suggest that inter-aggregate composition tends to stabilize near equimolar proportions regardless of the initial mass ratio, highlighting self-regulating behavior at the macro scale.