-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 106
-
Volume 105
-
Volume 104
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 106
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
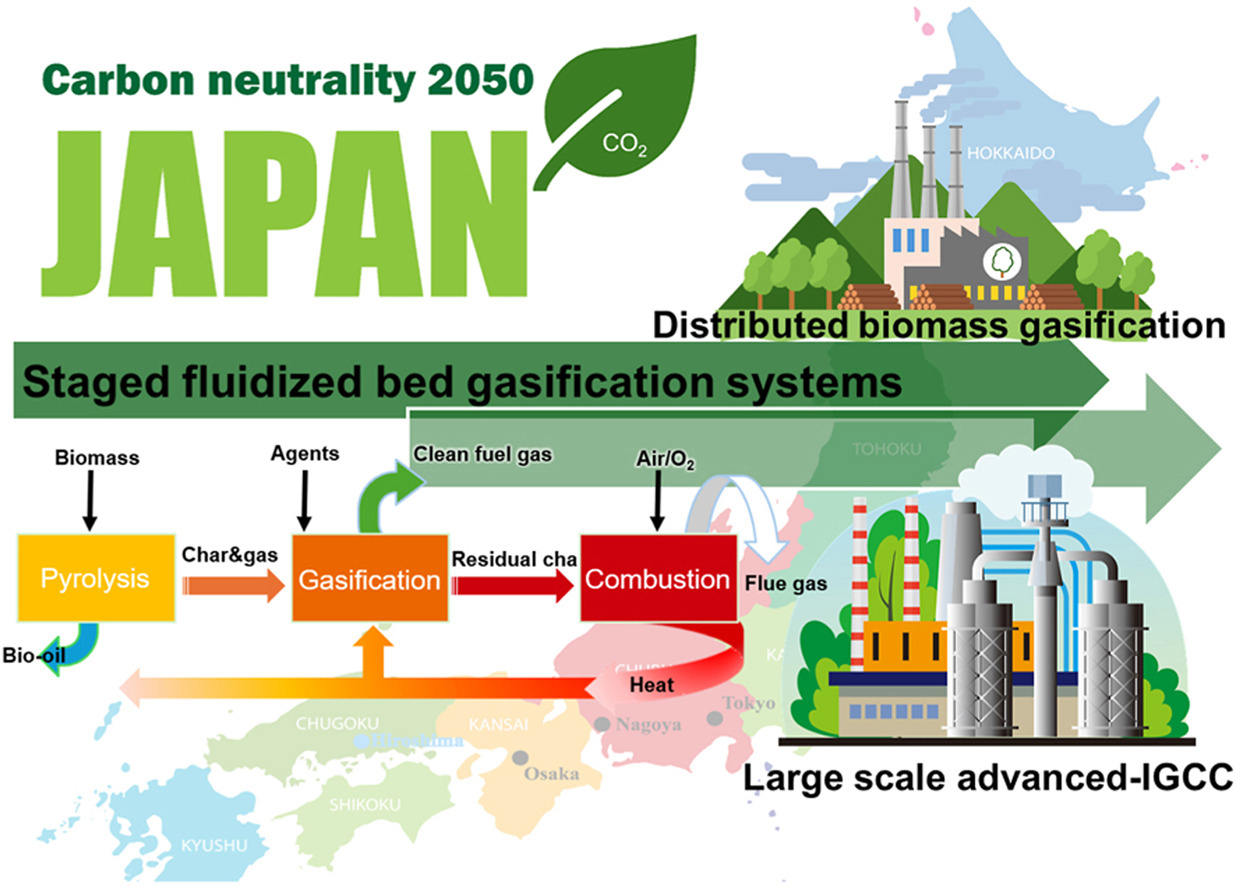
• Staged gasifiers achieve efficient reaction decoupling through sequential pyrolysis, gasification, and combustion.
• Research progress in Japan on staged gasification systems is comprehensively reviewed.
• Hydrodynamic and mixing studies verify stable solid circulation although scaling up remains challenging.
• Decentralized biomass gasifiers enable regional combined CHP generation and support carbon neutrality goals.
• Japan pioneered triple-bed gasifiers to suppress tar and improve syngas quality.
With the increasing imperative for carbon neutrality, gasification of carbon-based resources such as low-rank coal and/or biomass using fluidized-bed reactors has emerged as a pivotal process for generating clean syngas and hydrogen. However, conventional single-fluidized-bed reactors are limited by serious tar formation and low efficiency, which has motivated the development of staged systems that physically separate pyrolysis, gasification, and combustion. Japan has played a pioneering role in advancing dual fluidized bed (DFB) and triple-bed circulating fluidized bed (TBCFB) technologies, emphasizing reaction decoupling, thermal management, and process intensification. Unlike developments in other regions, Japanese research is characterized by the systematic integration of fundamental hydrodynamic studies, pilot-scale validation, and engineering innovations tailored to the nation's energy context. This review summarizes the theoretical foundations, hydrodynamic studies, pilot-scale demonstrations, and recent engineering innovations, including CO2-assisted gasification, and new cyclone pyrolyzers, developed in Japan. Despite the challenges associated with scale-up and system complexity, staged gasification has been demonstrated to offer distinct advantages in terms of syngas quality, tar suppression, and feedstock adaptability. The future of this field lies in decentralized, small-scale distributed systems integrated with the combined heat and power, in alignment with Japan's carbon neutrality roadmap and providing global insights into sustainable low-rank coal and biomass utilizations.