- Volumes 108-119 (2025)
-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 107
Pages 1-376 (December 2025)
-
Volume 106
Pages 1-336 (November 2025)
-
Volume 105
Pages 1-356 (October 2025)
-
Volume 104
Pages 1-332 (September 2025)
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 107
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Two novel hybrid micromixers designed: multi-channel and super-efficient types.
• Hybrid mixers integrate tree-shape distributor, SAR, and Focus mixer units.
• Hybrid micromixers produce ultra-high mixing efficiency (>97 %) across Re 0.5–120.
• SAR mixers achieve >90 % efficiency via Baker's transformation and secondary flow.
• Tree-shape distributor uniformly splits flow, and Focus mixer thins liquid lamellae.
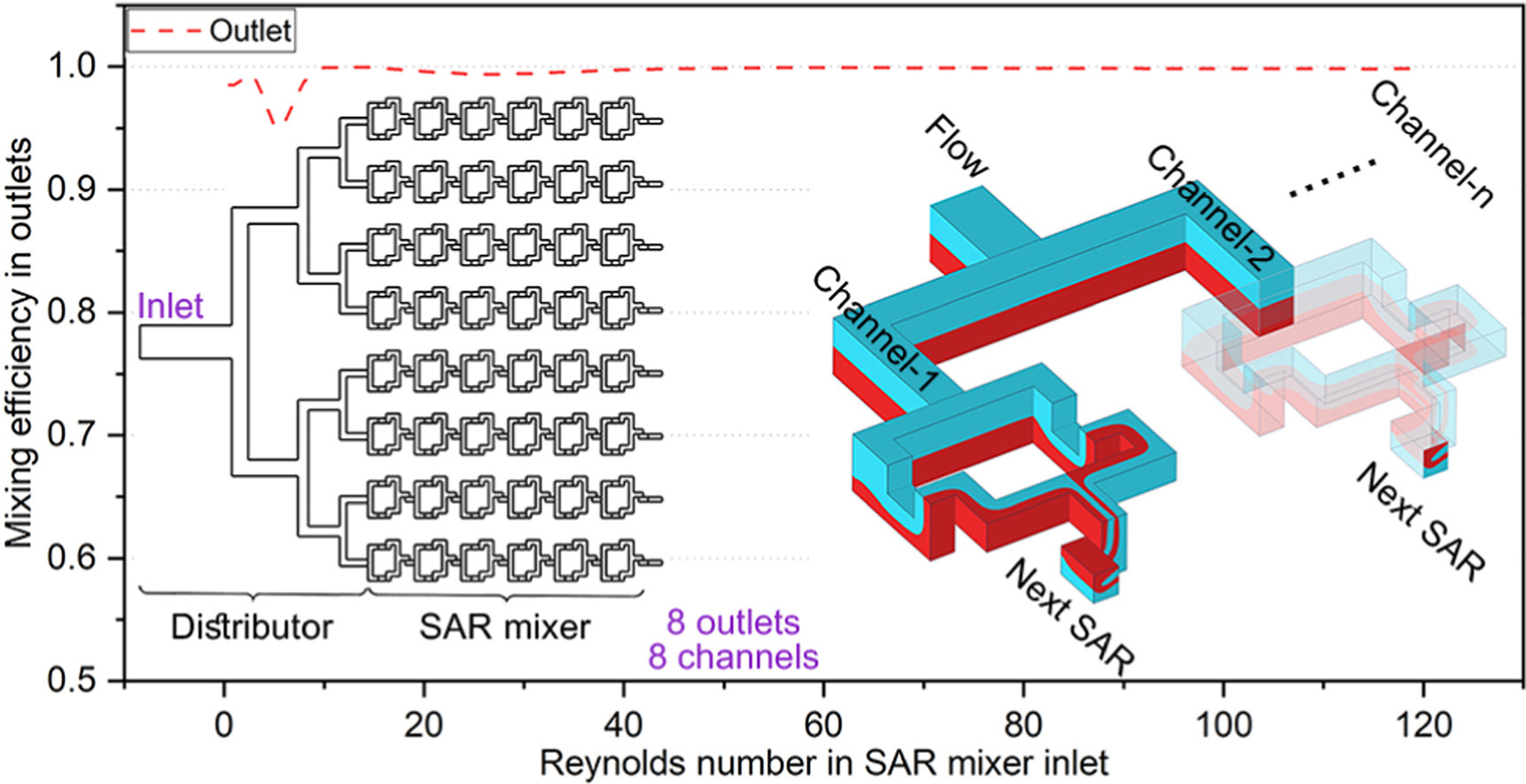
This study designs and analyzes two high-performance hybrid micromixers: a multi-channel type Mixer 1 and a super-efficient type Mixer 2. Mixer 1 integrates a tree-shape distributor with Split-and-Recombine (SAR) mixers, while Mixer 2 incorporates an additional tree-shape Focus mixer after the SAR mixers. Mixing performance was analyzed across a Reynolds number (Re) range of 0.5–120. The distributor, designed via entropy generation minimization, uniformly splits flow into eight outlets while preserving the inlet concentration distribution. The SAR unit significantly enhances transverse mass transport through Baker's transformation and secondary flows. Using over four SAR units yields >90 % efficiency across the entire Re range. The Focus mixer reduces fluid-layer thickness through bifurcation-merging processes and induces secondary flow; with four branching generations, its efficiency surpasses 90 % at Re > 10 and 99 % at Re > 35. In hybrid configurations with six SAR units, Mixer 1 exhibits a mixing efficiency dip to 95 % for Re = 6 across all outlets, exceeding 99 % for Re < 3 and Re > 8. Mixer 2 also shows a dip at Re = 6, but its minimum efficiency remains >97 %, validating its ultra-high-efficiency design.