- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
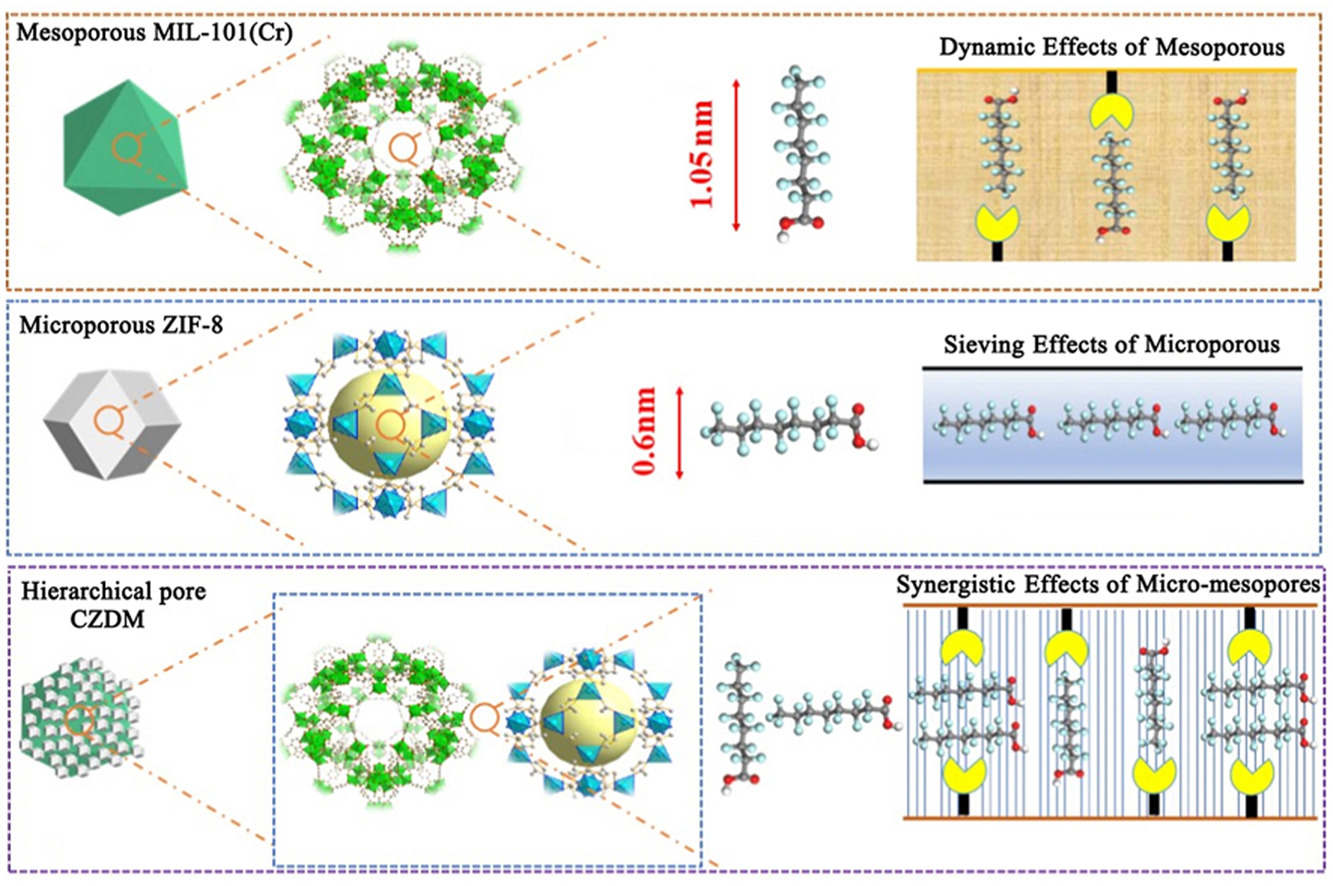
• A novel MIL-101(Cr)@ZIF-8 was first prepared and developed.
• MIL-101(Cr)@ZIF-8 exhibits excellent adsorption performances toward perfluorooctanoic acid.
• Synergistic effects of pores and bimetallic features enhance the adsorption performance.
Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) have gained widespread attention as potential adsorbents for the removal of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). However, single-component MOF often exhibit limitations in adsorption capacity, functionality, and pore structure. Hereby, we innovatively designed and synthesized a dual-metal core-shell MOF composite adsorbent, MIL-101(Cr)@ZIF-8 (a chromium-zinc bimetallic MOF, CZDM), which exhibits an excellent adsorption removal performance of PFOA from aqueous solutions. The results showed that the CZDM composite material has a high specific surface area (2091 m2/g), with pore structures exhibiting typical micropores (∼1.16 nm) and mesopores (∼3.4 nm), which are crucial for the efficient adsorption of PFOA. SEM and TEM images revealed that CZDM has a uniform core-shell morphology, with MIL-101(Cr) as the core and ZIF-8 as the shell, maintaining a stable and intact structure. EDX analysis further confirmed the successful incorporation of Cr and Zn elements. Batch experiments evaluated the effects of temperature, solution pH, and PFOA concentration on adsorption efficiency. The results demonstrated that the CZDM-3 adsorbent exhibited rapid adsorption kinetics and good PFOA removal efficiency across a wide pH range. The superior adsorption performance of CZDM is attributed to the synergistic effect of the dual-metal active sites, optimized pore structure, electrostatic interactions, and coordination bonds. The maximum adsorption capacity for PFOA reached 625.5 mg/g, with equilibrium achieved within 60 min, outperforming some related reported adsorbents. The experimental data of the adsorption process fit well with both Langmuir adsorption isotherms and pseudo-second-order kinetics models, indicating that the adsorption process is spontaneous, endothermic, and accompanied by an increase in entropy. Notably, even after five cycles, the CZDM material maintained high removal efficiency toward PFOA. This study advances a new synthesizing strategy of the MOF@MOF, and the CZDM exhibits a potential application in PFOA elimination from water.