- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
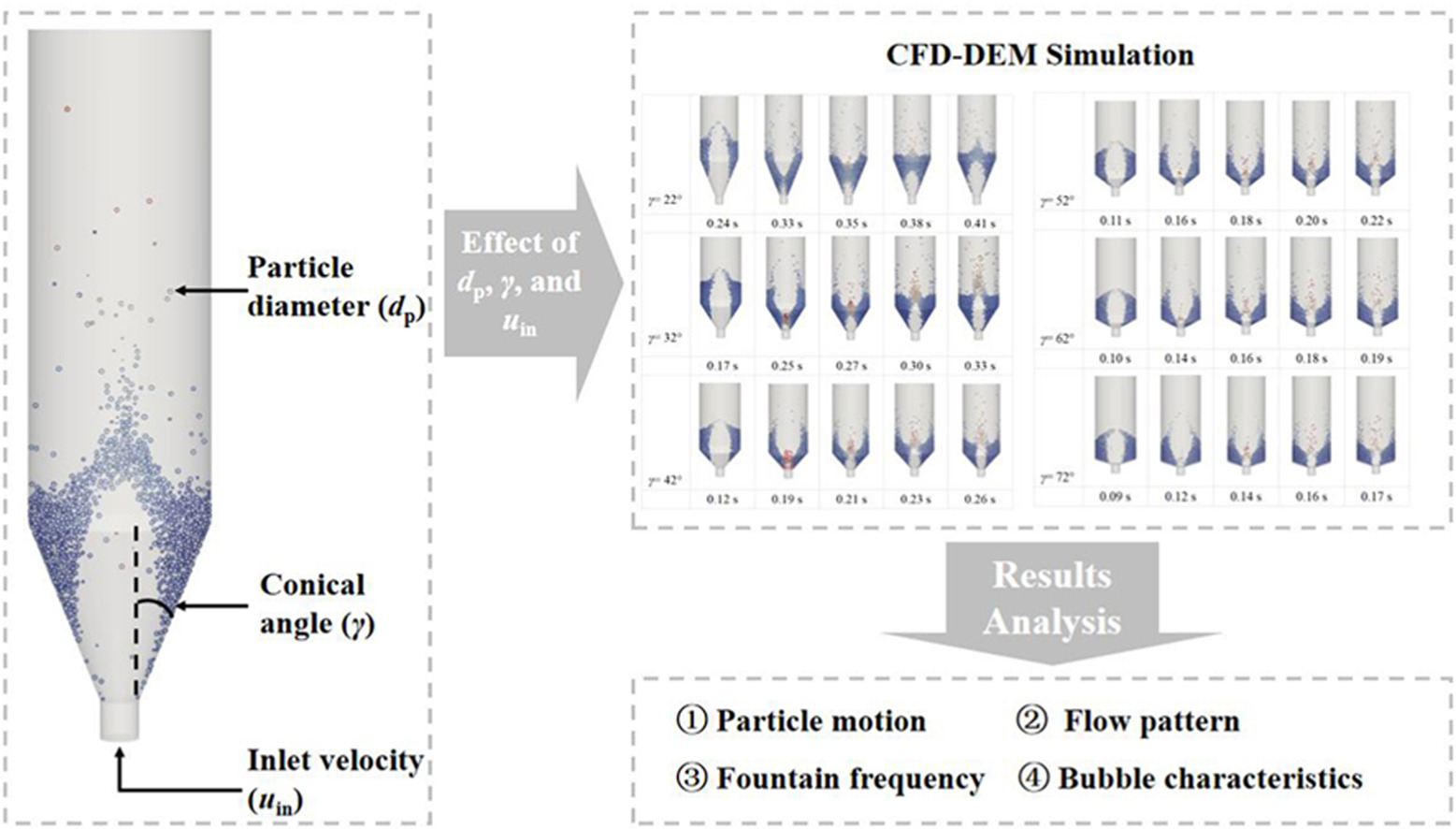
• Three operation parameters of the three-dimensional spouted bed are constructed.
• CFD-DEM model of particle spouted bed is established.
• Flow pattern, fountain frequency, and bubble characteristics are analyzed.
• Effect of conical angles under various operation condition are also examined.
• Differences caused by inlet gas velocity and particle diameter are explored.
A numerical investigation of the three-dimensional conical spouted bed was conducted using CFD coupled with discrete element method to systematically analyze particle-gas flow patterns, bubble volume fluctuations, and fountain characteristics. Moreover, the impact of conical angles on dynamic characteristics is demonstrated under varying gas inlet velocity and particle diameter. Firstly, the simulation result shows that increasing the conical angle is advantageous for enhancing both y-direction and angular velocities of particles, while the impact of this angle varies with inlet velocity and particle diameter. The great inlet velocity and particle diameter significantly enhance the voidage, while the larger conical angle promotes the uniform radial particle distribution. Besides, smaller conical angle and medium inlet velocity is prone to result in the higher frequency and amplitude for the fluctuations of particle height. Meanwhile, enlarging the conical angle results in a shift of the fountain frequency from high to low when the particle size is small. The conical angle plays a crucial role in determining bubble behavior under the condition of medium velocity and small diameter. Besides, the fine particle and small conical angle are prone to cause the noticeable main frequencies.