- Volumes 108-119 (2025)
-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 107
Pages 1-376 (December 2025)
-
Volume 106
Pages 1-336 (November 2025)
-
Volume 105
Pages 1-356 (October 2025)
-
Volume 104
Pages 1-332 (September 2025)
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 107
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
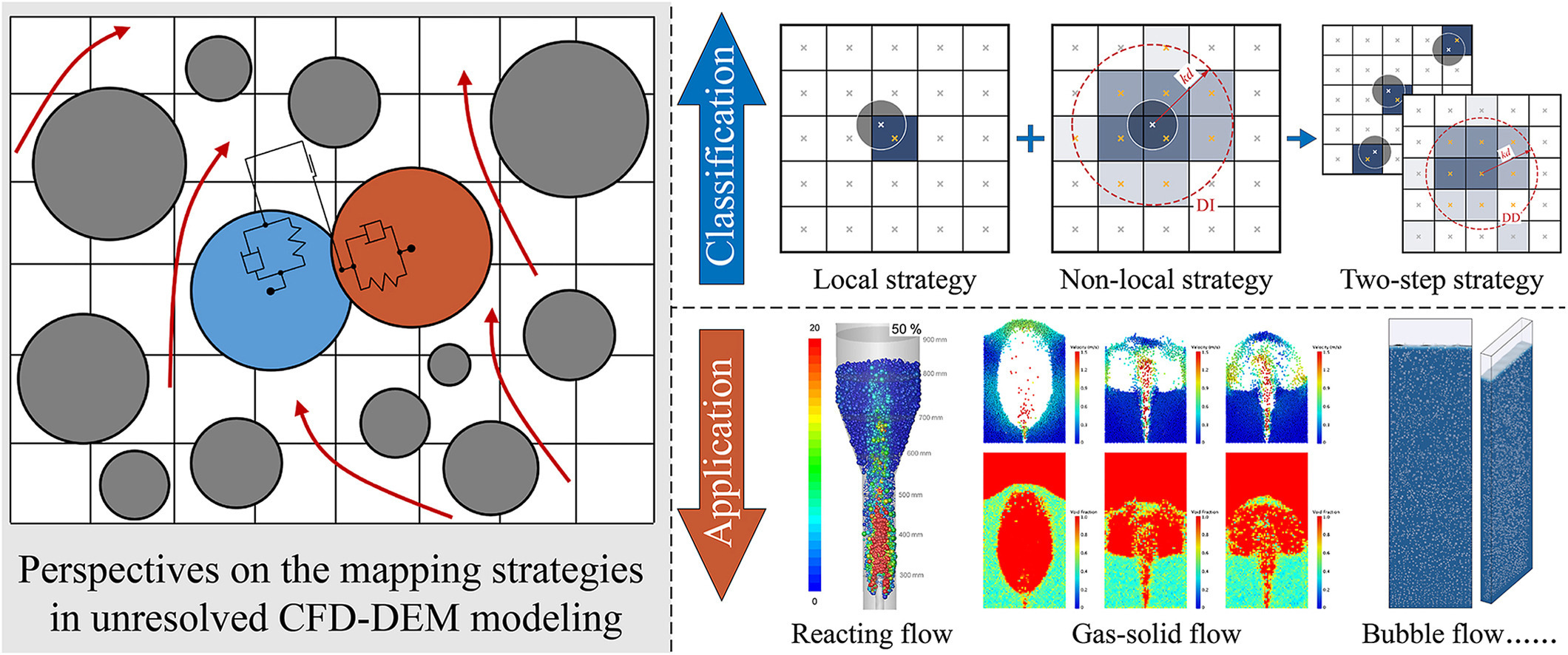
• A systematic perspective on mapping strategies for unresolved CFD-DEM modeling.
• Summarize and analyze the merits and limitations of local, non-local, and two-step mapping schemes.
• Identify key challenges and future directions of developing novel mapping schemes.
The accurate transfer of discrete particle information to continuum Eulerian fields, known as mapping or coarse-graining, plays a critical role in unresolved CFD-DEM modeling, governing both numerical stability and physical fidelity. Over the years, a variety of strategies have been proposed, spanning from local methods such as the satellite point scheme to non-local approaches based on kernel functions, diffusion, or hybrid formulations. Each method balances trade-offs between smoothness, conservation, computational efficiency, and applicability to complex grid configurations or non-spherical particles. This perspective summarizes the general methodology, representative implementations, and typical applications of existing mapping algorithms, and analyzes their respective merits and limitations. Particular attention is given to challenges associated with small grid-to-particle size ratios, irregular geometries, computational costs, and multi-physics coupling. Emerging directions, including adaptive and hybrid schemes, consistency with turbulence modeling, extensions to polydisperse and non-spherical particles, and machine learning-aided mapping acceleration, are discussed. Continued efforts in these areas promise to improve the robustness, accuracy, and scalability of CFD-DEM simulations, ultimately enabling more generalized and reliable modeling of complex multiphase flows in both research and industrial applications.