- Volumes 108-119 (2025)
-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 107
Pages 1-376 (December 2025)
-
Volume 106
Pages 1-336 (November 2025)
-
Volume 105
Pages 1-356 (October 2025)
-
Volume 104
Pages 1-332 (September 2025)
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 107
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
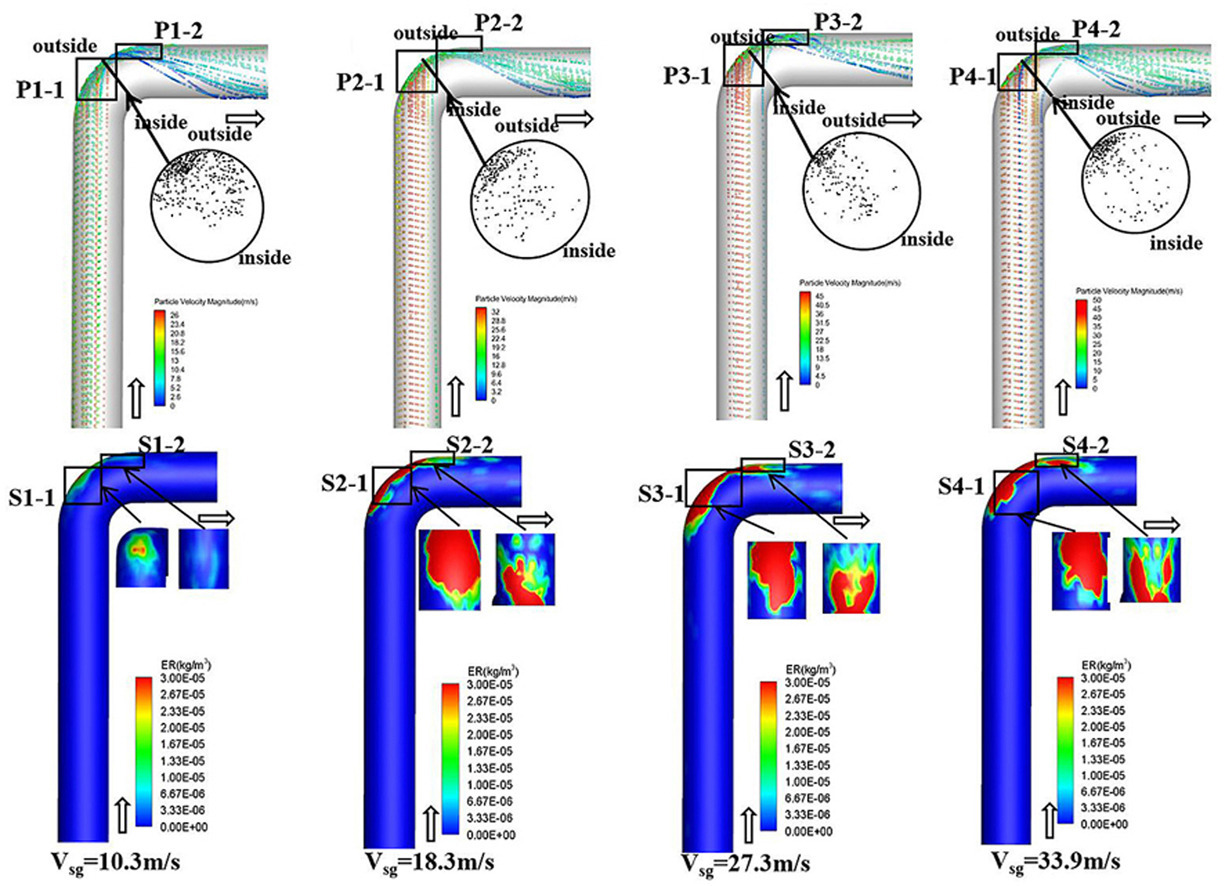
• Volume of fluid (VOF) coupling with DPM is employed to simulate gas-liquid-solid flow in a vertical-horizontal elbow.
• Erosion behavior of multiphase flow in the elbow is predicted by means of Oka model.
• Existence of liquid film enhances the resistance of particles and curtails the erosion rate.
• Increments in gas velocity and the Stokes number prompt the particles to deviate from the fluid streamline.
In the process of natural gas exploitation and transportation, the problem of pipeline erosion and wear due to gas-liquid-solid three-phase flow is widespread. The repetitive impact of sand particles against the pipe wall results in the weakening of the wall surface, and the consequences are perforation or even leakage, posing a significant risk to both production and the environment. In this study, the volume of fluid (VOF) multiphase flow model in conjunction with the discrete phase model (DPM) is employed to simulate the particle flow behavior of gas-liquid-solid multiphase flow in vertical-horizontal elbow. Furthermore, the erosion behavior of multiphase flow in the elbow is studied by means of the Oka model. The predicted void fraction of gas and erosion rate are in good agreement with the experimental results measured by Parsi et al. Furthermore, the influence laws of liquid film, gas velocity, particle size and particle mass flow rate on elbow erosion have been obtained. The findings indicate that the existence of liquid film enhances the resistance of particles, curtails the erosion rate, and exerts a buffering effect on erosion. The gas velocity and the Stokes number rise, prompting the particles to deviate from the fluid streamline and their collision velocity to augment. While the inertia force of the particles intensifies, and the buffering impact of the liquid film diminishes with an increase of the particle size. Also, the variation trend in the number of particles is in line with the probability of collision and the size of the collision region.