- Volumes 108-119 (2025)
-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 107
Pages 1-376 (December 2025)
-
Volume 106
Pages 1-336 (November 2025)
-
Volume 105
Pages 1-356 (October 2025)
-
Volume 104
Pages 1-332 (September 2025)
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 107
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
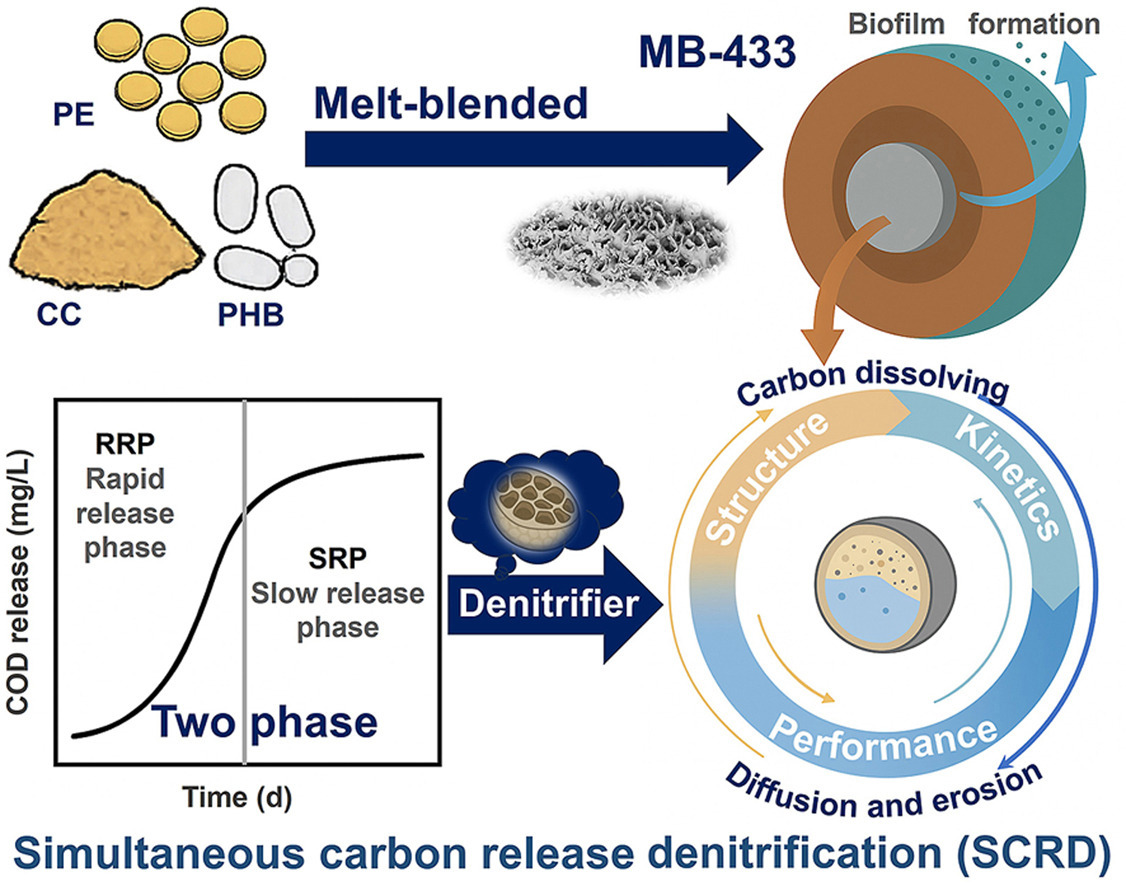
• Melt-blended advanced carbon sources were developed and achieved SCRD to treat low-C/N wastewater.
• Particle porosity and surface roughness identified as key factors controlling carbon-release kinetics.
• Optimized PHC-433 achieved high nitrate removal, avoided inhibition, and sustained long-term performance.
• Kinetic analysis validated the simultaneous carbon release-denitrification behavior of PHC-433.
Achieving simultaneous carbon release and denitrification (SCRD) remains a key challenge for solid carbon sources (SCSs) in low-C/N wastewater treatment. In this project, novel melt-blended advanced carbon sources (MB-ACSs) with tunable compositions were developed to regulate SCRD through structural design, where MB-ACSs were engineered to form interpenetrating networks with controllable porosity and diffusivity based on the different compositions of corn cob (CC) and polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) within a polyethylene (PE) matrix. Among them, MB-433 (40 wt% PE, 30 wt% PHB, 30 wt% CC) exhibited the most balanced structure, integrating rapid CC-derived dissolution, PHB-mediated sustained release, and PE-supported stability. All MB-ACSs displayed a biphasic release pattern – initial surface dissolution followed by internal diffusion – whereas MB-433 maintained a steady carbon supply ideally synchronized with microbial demand. Denitrification assays conducted across a wide range of nitrate loads (25–1000 mg NO3−-N/L) and C/N (0, 1.5, 3) showed that MB-433 consistently achieved 60–80 % nitrate removal under moderate conditions (25–50 mg NO3−-N/L), avoided inhibition under high-loading and high-carbon conditions (1000 mg NO3−-N/L, C/N = 3), and maintained complete denitrification even in the absence of external carbon (C/N = 0). Logistic and exponential fittings confirmed MB-433's superior capacity on SCRD, while Monod modeling revealed high denitrification potential (Vmax = 0.172 mg/L d) and strong nitrate affinity (Ks = 8.42 mg/L).