-
文章精选
- 当期目录
-
过刊浏览
-
Volumes 108-119 (2025)
-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
Pages 1-332 (September 2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volumes 54-59 (2021)
-
Volumes 48-53 (2020)
-
Volumes 42-47 (2019)
-
Volumes 36-41 (2018)
-
Volumes 30-35 (2017)
-
Volumes 24-29 (2016)
-
Volumes 18-23 (2015)
-
Volumes 12-17 (2014)
-
Volume 11 (2013)
-
Volume 10 (2012)
-
Volume 9 (2011)
-
Volume 8 (2010)
-
Volume 7 (2009)
-
Volume 6 (2008)
-
Volume 5 (2007)
-
Volume 4 (2006)
-
Volume 3 (2005)
-
Volume 2 (2004)
-
Volume 1 (2003)
-
Volumes 108-119 (2025)
-
高被引
-
高下载
-
特邀文章
-
专刊合集
-
待刊文章
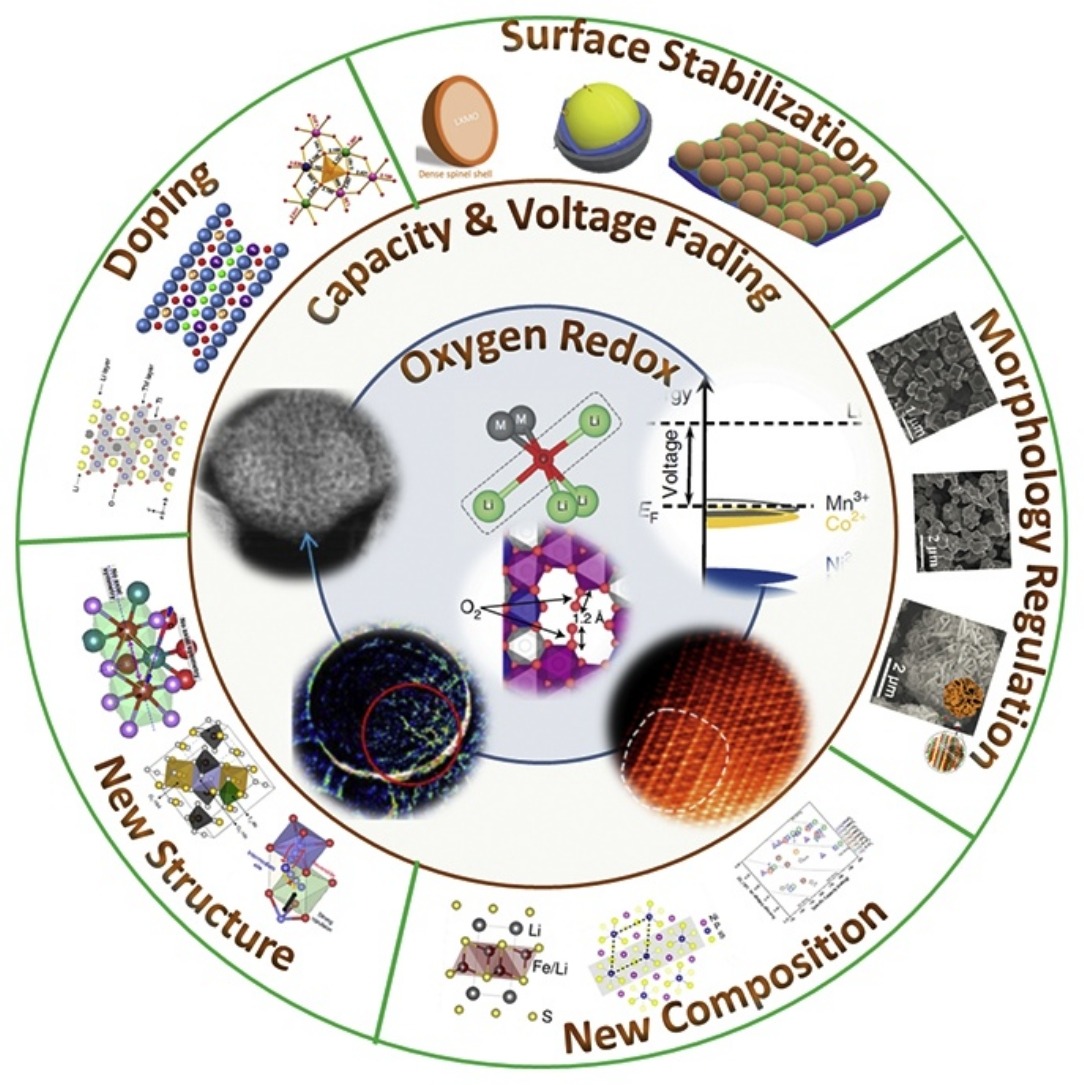
• The structure and performances of Li-rich layered oxides are introduced.
• Mechanisms of oxygen loss, capacity fading and voltage fading are reviewed.
• Strategies to mitigate capacity and voltage fading are summarized.
Lithium rich layered oxides (LLOs) are attractive cathode materials for Li-ion batteries owing to their high capacity (>250 mA h g–1) and suitable voltage (∼3.6 V). However, they suffer from serious voltage and capacity fading, which is focused in this review. First, an overview of crystal structure, band structure and electrochemical performances of LLOs is provided. After that, current understanding on oxygen loss, capacity fading and voltage fading is summarized. Finally, five strategies to mitigate capacity and voltage fading are reviewed. It is believed that these understandings can help solve the fading problems of LLOs.